Java-CurrentHashMap高并发实践探索
在高并发写(增/删)的场景下jdk1.7的CurrentHashMap会发生什么问题呢,以下会为你一一解答。
Let’s Go!
1.解决方案
- 可用hashmap+rwlock代替,写性能因写锁范围影响,不会太高。
- 升级jdk 1.8,jdk1.8的remove操作已改成:删除一个节点,将前一节点的next指针指向当前删除节点的next。(推荐)
2.场景
消息系统推送消息量约300-400/s
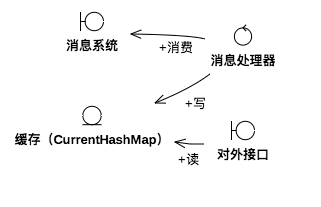
3.环境
- jdk1.7.0
- CentOS release 6.3 (Final) 2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64
- Cpu :24 (Intel E5-2420 v2@2.2G)
- Mem :64G (App占用4G)
4.问题现象
- Full GC 较多(一天几次)
- Young GC 频繁
- jmap内存监控显示Integer类型过多
错误信息
无
GC信息
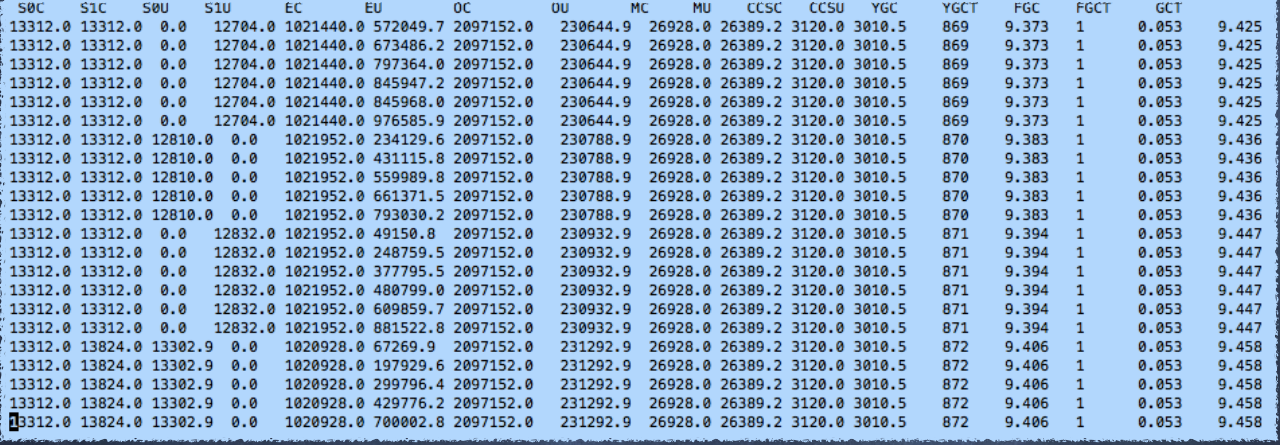
从中看出ygc次数较多,并花费时间较长。(fullgc截图没了)
5.问题分析
初步分析
- Integer类型过多,发现引用是来自 concurrenthashmap
- 修改其中concurrenthashmap为hashmap之后 Integer对象大幅减少
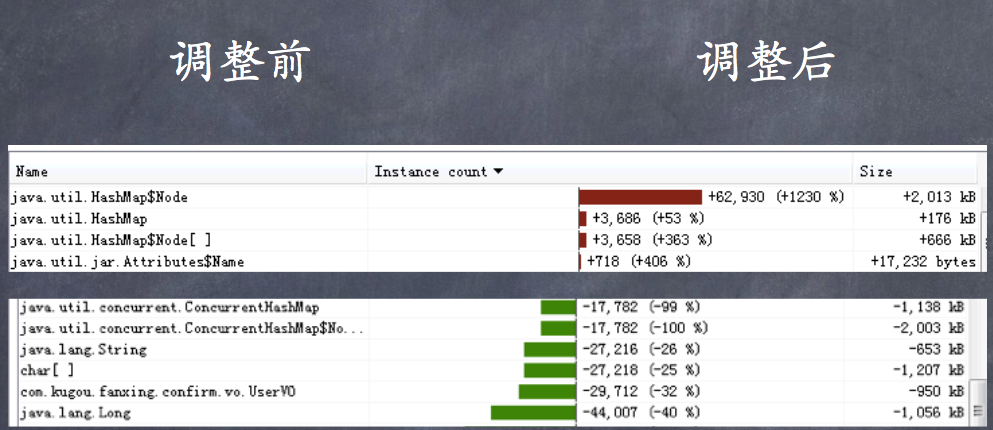
- 但young gc次数没变
深入分析
- 为什么Integer类型过多并引用是来自 concurrenthashmap?
问题就在于 concurrenthashmap.remove的逻辑,请看【代码1】
如在链表中间删除节点如下图:
删除前:
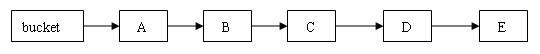
删除后:
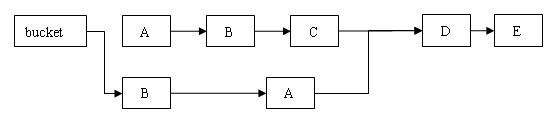
如图所示,旧的A,B,C节点都成为了垃圾
代码1:
final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
if (!tryLock())
scanAndLock(key, hash);
V oldValue = null;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> e = entryAt(tab, index);
HashEntry<K,V> pred = null;
while (e != null) {
K k;
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
if (pred == null)
setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
else
pred.setNext(next);
++modCount;
--count;
oldValue = v;
}
break;
}
pred = e;
e = next;
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
- 为什么修改其中concurrenthashmap为hashmap之后 Integer对象大幅减少?
参考【为什么Integer类型过多并引用是来自 concurrenthashmap】
因key为Integer类型,使用remove方法删除其节点后,会出现大量垃圾内存。所以表现为Integer大量增多
将 concurrenthashmap 更换为 hashmap 后,Integer对象即大幅减少。

Written on May 15, 2016